머신러닝 (ML)
미래에 관한 예측분석이 목표.
ex.) 영화 추천, 음식 주문
- 지도 학습
- 이미 알려진 사례를 바탕으로 일반화된 모델을 만들어 의사 결정 프로세스를 자동화 하는 것.
- 지도 학습 알고리즘
- 입력과 출력으로부터 학습하는 머신러닝 알고리즘
- 분석하기도 좋고 성능을 측정하기도 좋다.
- 비지도 학습 알고리즘
- 입력을 주어지지만 출력은 제공되지 않음.
- ex). 블로그 글의 주체 구분, 고객들의 취향이 비슷한 그룹으로 묶기.
- 지도 학습과 비지도 학습
- 컴퓨터가 인식할 수 있는 형태로 데이터 준비
- 열 (속성) -> 특성(Feature)
- 행 (데이터) -> 샘플(Sample), 데이터 포인트(Data point)
오픈소스 싸이킷런(scikit-learn)
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/
scikit-learn: machine learning in Python — scikit-learn 1.2.2 documentation
Model selection Comparing, validating and choosing parameters and models. Applications: Improved accuracy via parameter tuning Algorithms: grid search, cross validation, metrics, and more...
scikit-learn.org
pip install numpy scipy matplotlib ipython scikit-learn pandas pillow imageiopython: 3.9.13 (main, Aug 25 2022, 23:51:50) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)]
pandas: 1.4.4
matplotlib: 3.5.2
NumPy 1.21.5
SciPy: 1.9.1
IPython: 7.31.1
scikit-learn 1.0.2SciPy
고성능 선형 대수, 함수 최적화, 신호 처리, 특수한 수학 함수와 통계 분포 등을 포함한 많은 기능 제공.
희소 행렬

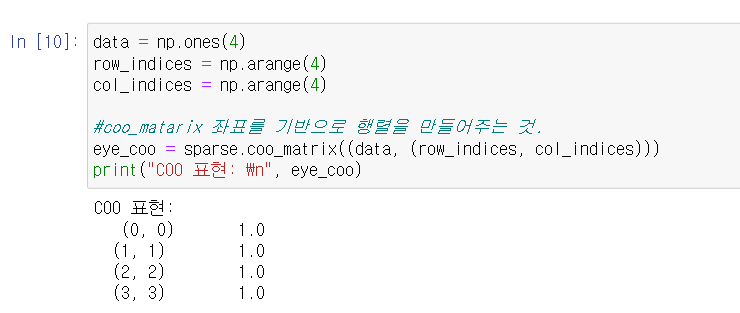
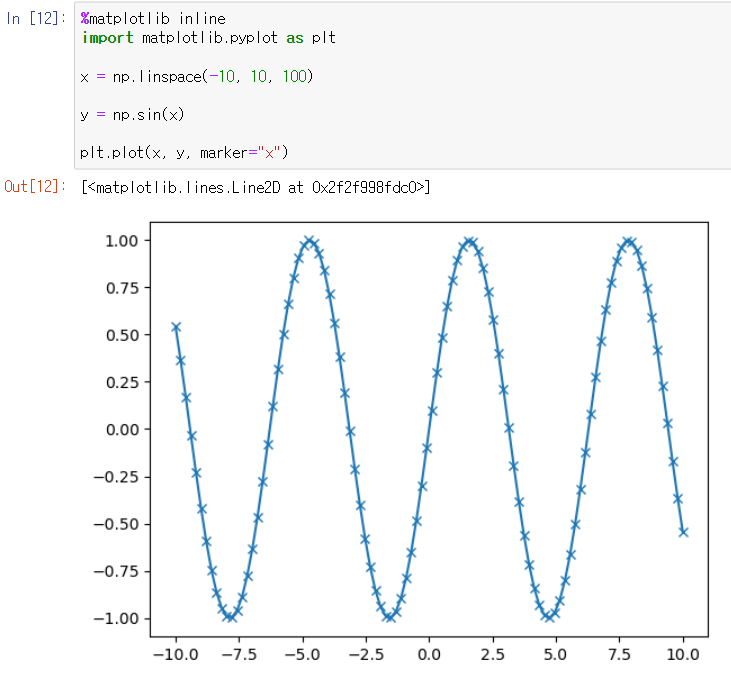
Matplotlib
- 과학 계산용 라이브러리
- 선 그래프, 히스토그램, 산점도 등을 지원.
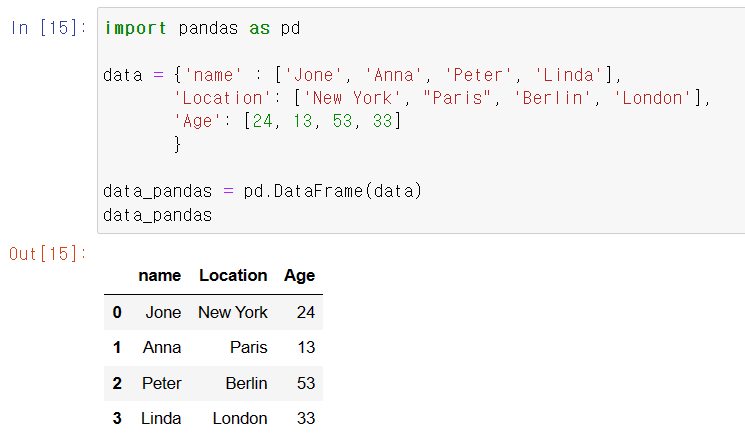
Pandas
- 클래스의 도출
- 출력될 수 있는 값.
- ex). 붓꽃의 종류
- 레이블
- 데이터 포인트 하나에 대한 기대 출력
- ex). 데이터 포인트 하나(붓꽃)에 대한 기대 출력은 꽃의 품종이됨.
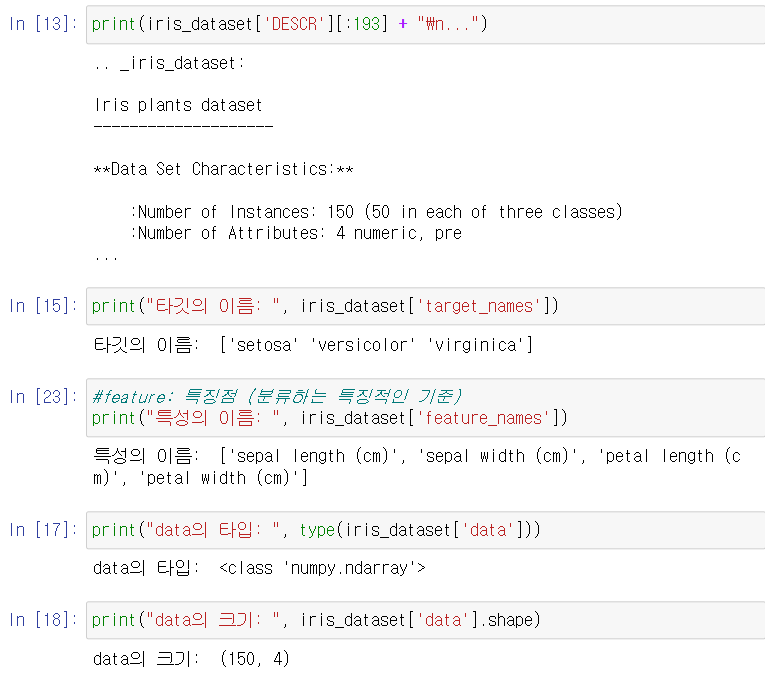
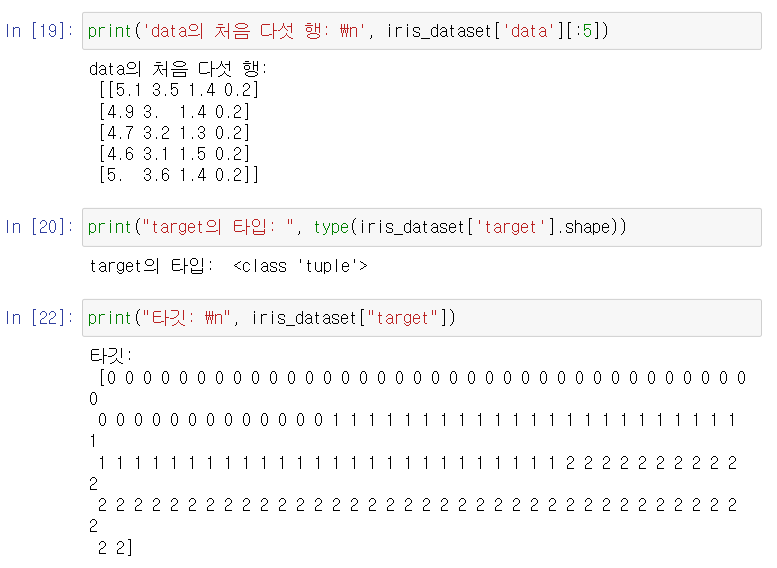
성과 측정
머신러닝 모델을 만들고 새로운 데이터의 품종을 예측하려 함.
train_test_split( )
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(arrays,
test_size, train_size, random_state, suffle, stratify)
| 속성 | 내용 |
| arrays | 분할시킬 데이터 입력 |
| test_size | 테스트 데이터셋의 비율(float), 갯수(int) |
| train_size | 학습 데이터셋의 비율(float), 갯수(int) |
| random_state | 데이터 분할 시 셔플이 이루어지는 시드 값. |
| shuffle | 셔플 여부 결정 (defalt = True) |
| stratify | 지정한 Data에 비율 유지. |
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
iris_dataset['data'], iris_dataset['target'], random_state=0)
iris_dataframe = pd.DataFrame(X_train, columns=iris_dataset.feature_names)
pd.plotting.scatter_matrix(iris_dataframe,
c = y_train,
figsize = (15,15),
marker = 'o',
hist_kwds = {'bins':20},
s = 60,
alpha = .8,
cmap = mglearn.cm3)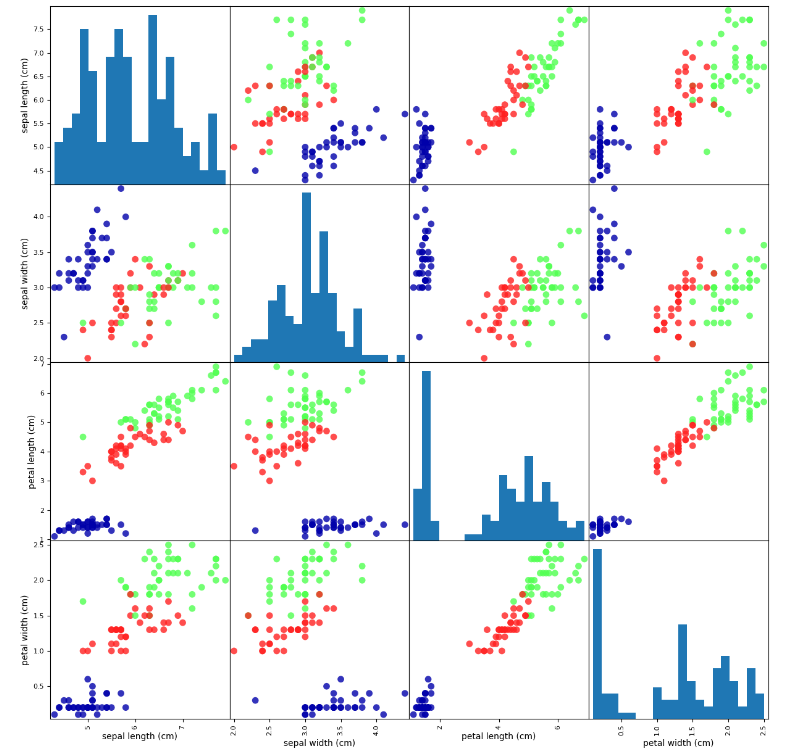
k-최근접 이웃 알고리즘
- 단순히 훈련 데이터를 저장하여 만들어짐.
- 새로운 데이터 포인트에 대한 예측이 필요하면 알고리즘은 새 데이터 포인트에서 가장 가까운 훈련 데이터 포인트를 찾음.
- 새 테이터 포인 포인트에 가장 가까운 'k개'의 이웃을 찾는다.
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = 1)
# X : 꽃받침 ... 크기
# y: 품종 정보
예측하기
- knn.predict( )
- 꽃받침의 길이가 5cm, 폭이 2.9cm, 꽃잎의 길이기 1cm, 폭이 0.2cm인 붓꽃의 품종 예측.

모델 평가하기
- 정확도를 계산하여 모델의 성능을 평가.

과대 적합...
지도 학습
X, y = mglearn.datasets.make_forge()
mglearn.discrete_scatter( X[:, 0], X[:, 1], y)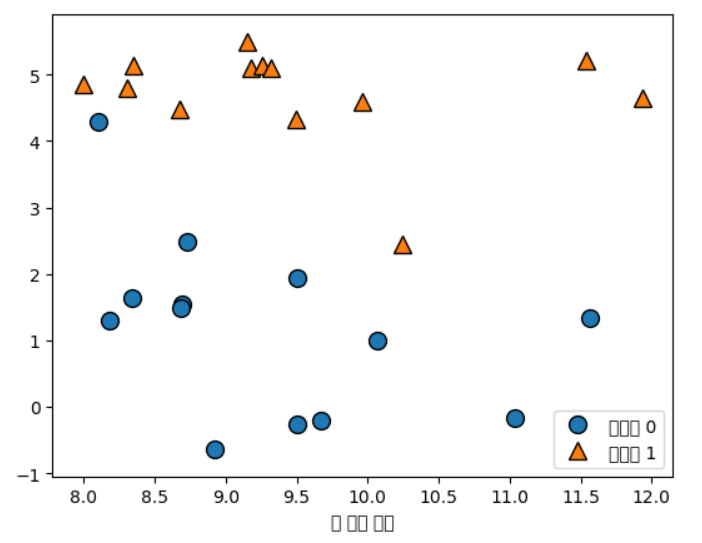
X, y = mglearn.datasets.make_wave(n_samples=40)
plt.plot(X, y, 'o')
plt.ylim(-3,3)
plt.xlabel("Feature")
plt.ylabel("Target")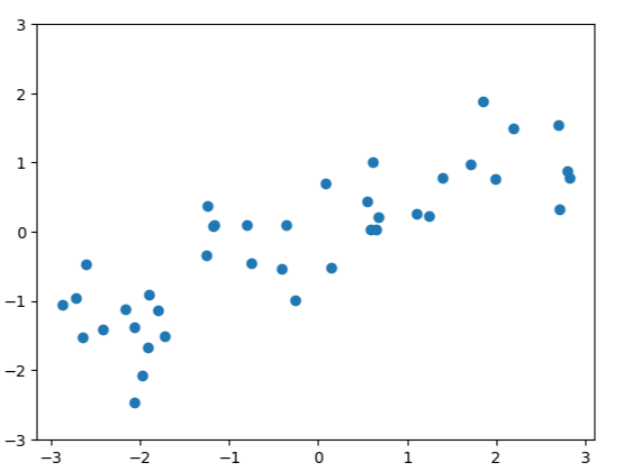
유방암 데이터셋을 활용한 지도 학습
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
cancer = load_breast_cancer()
print("cancer.keys():", cancer.keys())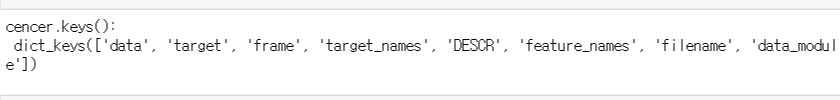

k-최근접 이웃
- 알고리즘이 훈련 데이터셋에서 가장 가까운 데이터 포인트, '최근접 이웃'을 찾음.
# 이웃의 수 1개
mglearn.plots.plot_knn_classification(n_neighbors = 1)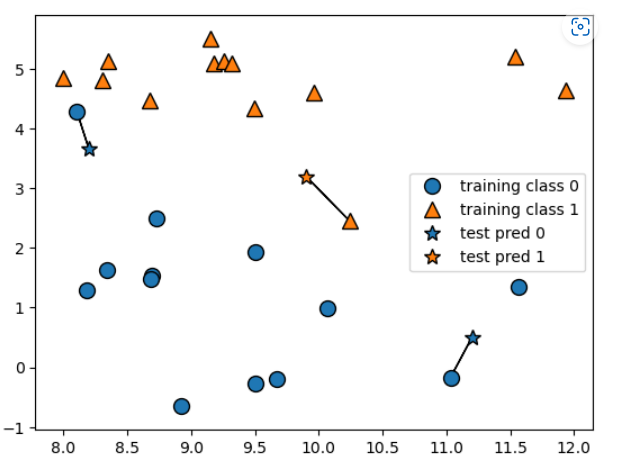
# 이웃의 수 3개
mglearn.plots.plot_knn_classification(n_neighbors = 3)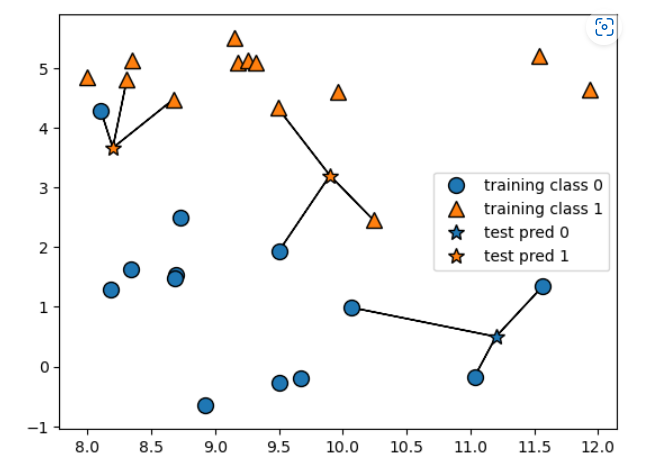
- 이웃을 늘릴수록 일반화 성능이 올라감.
- 하지만, 너무 늘리면 과소적합 상태가 됨.
- 이웃은 5~6개 사이가 제일 적합함.
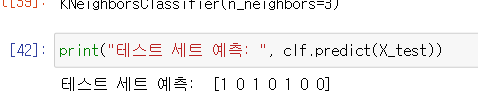
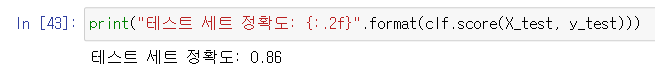
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X, y = mglearn.datasets.make_forge()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state = 0)from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = 3)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
KNeighborsClassifier 분석
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize = (10, 3))
for n_neighbors, ax in zip([1,3,9], axes):
clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = n_neighbors).fit(X, y)
mglearn.plots.plot_2d_separator(clf, X, fill = True, eps = 0.5, ax = ax, alpha = .4)
mglearn.discrete_scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], y, ax = ax)
ax.set_title("{} neighbors".format(n_neighbors))
ax.set_xlabel("Feature 0")
ax.set_ylabel("Feature 1")
axes[0].legend(loc = 3)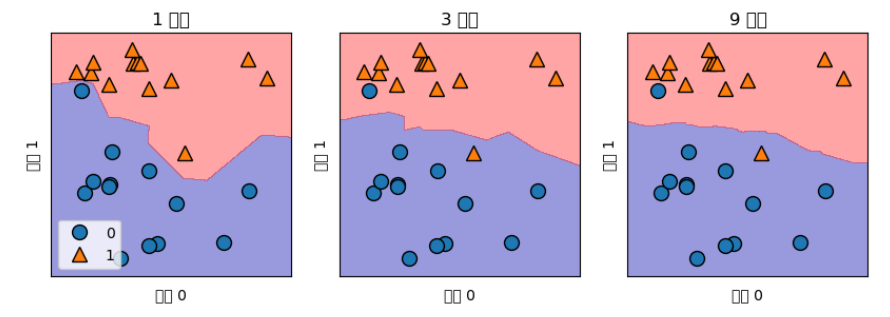
- 이웃의 수를 늘릴수록 결정 경계는 더욱 부드러워짐.
- 이웃을 적게 사용하면 복잡도가 올라가고, 이웃을 많이 사용하면 복잡도가 낮아짐.
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
cancer = load_breast_cancer()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
cancer.data, cancer.target, stratify=cancer.target, random_state=66)
training_accuracy = []
test_accuracy = []
neighbors_settings = range(1,11)for n_neighbors in neighbors_settings:
clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=n_neighbors)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
training_accuracy.append(clf.score(X_train, y_train))
test_accuracy.append(clf.score(X_test, y_test))
plt.plot(neighbors_settings, training_accuracy, label="Train Accuracy")
plt.plot(neighbors_settings, test_accuracy, label="Test Accuracy")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy")
plt.xlabel("n_neighbors")
plt.legend()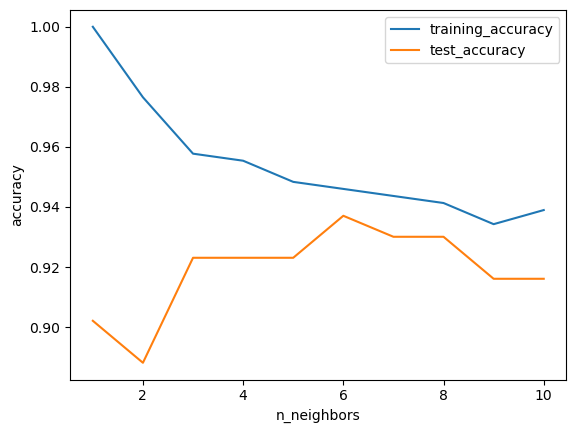
'ABC 부트캠프 > 머신러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 20일차 - 지도학습 3 (0) | 2023.04.12 |
|---|---|
| 19일차 - 지도학습 2 (1) | 2023.04.12 |
| 18일차 - 지도학습 1 (0) | 2023.04.11 |



댓글